Aging is a highly complex physiological phenomenon caused by both genetic and environmental factors. As we age, many biological processes in our bodies change and become less effective. Predictable changes include age-associated systemic inflammation and a decrease in repair/maintenance responses to stressors. Understanding the underlying causes of aging will lead to the development of new interventions against age-related challenges.
Population aging has become a worldwide phenomenon. It is projected that by 2030, 1 out of every 5 Americans will be of retirement age. Nearly all age-related disorders are associated with inflamm-aging – the inflammation that occurs throughout the aging process – which can affect the brain and nervous system. As aging progresses, the neurons lose the ability to communicate as abnormal accumulation of beta-amyloid aggregates and tau proteins interfere with the electrical signals responsible for brain activity. Some also experience vascular changes in the brain accompanied by glucose deficiencies and abnormal inflammation. Vascular changes in the brain and complications with glucose metabolism often leads to impairment of both function and growth(1). These neurological changes in the brain lead to impaired decision-making, learning, and motor delays. Simple tasks such as remembering the birthday of a loved one, anniversaries, and special occasions become an imminent challenge. Case in point, when is your mom’s birthday?
Inflammation and Theracurmin®
Epidemiological studies of Alzheimer’s disease suggest that populations with a high consumption of dietary curry have better memory performance and cognitive function. It is believed that the curcumin content of curry may potentially have neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory benefits.
What Is Curcumin?
Curcumin has been used for centuries as a part of a healthy diet that maintains overall well-being. While diets high in curcumin show promise against inflamm-aging, diets high in isolated curcumin (via supplementation) did not due to low oral bioavailability. As an isolate, a substantial fraction of curcumin is not absorbed by the body, therefore providing a very limited therapeutic result. Low bioavailability is commonly associated with oral dosage forms of poorly water-soluble supplements and is assessed by measuring the plasma concentration after a single dose.
Why You Should Choose Theracurmin®
To overcome low bioavailability, efforts to increase the water-solubility of curcumin were made. Theravalues Corporation based in Japan, developed (and patented) an innovative technique to improve the bioavailability and water dispersibility of curcumin called proprietary submicron particle processing and surface-controlled technology. This is what makes Theracurmin® 42.6x more bioavailable than regular curcumin preparations (2). In other words, a curcumin product on the shelf with standard curcumin powder content of 1000mg given twice a day will yield 2,000mg of curcumin, while Theracurmin with 90mg given once a day will yield 3,834mg of curcumin (90mg x 42.6 = 3,834mg).
The high bioavailability allows for a more potent formula in smaller amounts, achieving high efficacy and a convenient option for those tired of taking multiple pills a day. Theracurmin’s® patented technology preparation is highly water dispersive and can be incorporated in a variety of preparations like capsules, tablets, gummies, and nutritional powders.
In line with the company’s values, Theracurmin® is committed to assist a purpose-driven life with its superior bioavailability supported by over 30 clinical evidence including:
Liver function (https://ffhdj.com/index.php/ffhd/article/view/794)
Cardiovascular: arteries (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1872931212000592)
Cardiovascular: vascular (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0271531712001844?via%3Dihub)
Central arterial hemodynamics (https://academic.oup.com/ajh/article/25/6/651/2282053)
Respiratory: pulmonary (https://www.dovepress.com/highly-absorptive-curcumin-reduces-serum-atherosclerotic-low-density-l-peer-reviewed-fulltext-article-COPD)
Joints: gonarthrosis and coxarthrosis (https://theravalues.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/TC045.pdf)
Joint Health, exercise type on pain (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5747204/pdf/jer-13-6-684.pdf)
Joint Health, 6-month open label study (https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/1179544120948471)
Joint Health, in knee (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0949265815301913?via%3Dihub)
Muscle recovery: ingestion timing, muscle soreness (https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jnsv/65/1/65_82/_pdf/-char/en)
Ingestion timing, muscle damage and inflammation (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/sms.13373)
Attenuation of muscle damage (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00421-015-3170-4)
Brain: chemobrain (https://www.dovepress.com/the-effect-of-theracurmin-on-cognitive-function-in-an-older-patient-wi-peer-reviewed-fulltext-article-CIA)
Memory and brain amyloid and tau effects (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1064748117305110?via%3Dihub)
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and cognition in mental health (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0920996417306084)
With fatty acids on tumor necrosis factor (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00251-017-0992-8)
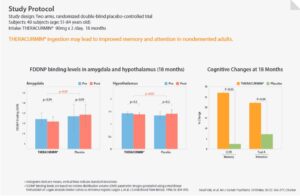
Dr. Gary Small, a Professor and Medical Specialist at UCLA and Hackensack University Medical Center tested the effects of Theracurmin® in over 40 participants. The participants were overall healthy, with normal age-related changes in cognition in addition to no signs of dementia. The 40 participants were divided into two groups, with half the participants receiving Theracurmin® twice daily, the other a placebo. The two groups participated in verbal reminding tests, visual memory tests, and attention tests every six months for 18 months. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans were also conducted on the brains of the participants to look for markers of Alzheimer’s disease such as beta-amyloid plaques and tau proteins.
Overall, participants taking Theracurmin® demonstrated:
- Significant memory improvement after 18 months compared to participants receiving placebo
- PET scans with lower levels of beta-amyloid and tau in the brain, which are proteins that play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disease
- Theracurmin® can provide significant cognitive benefits over time (3)
A retrospective follow-up study was published in September 2021 to analyze Theracurmin’s® further effect on memory and attention in older adults with Alzheimer’s disease. 93 patients with Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment (MCI), which can be an early indicator of Alzheimer’s disease, underwent geriatric assessment at the beginning and end of a 6-month trial period. The assessment included common cognitive screening tests such as the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MOCA), activities of daily living (ADL), and Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE). 17 patients with MCI and 19 with Alzheimer’s received a daily dose of Theracurmin®. At the end of the 6 months period, patients not treated with Theracurmin® showed a decline in MOCA, instrumental ADL, and MMSE scores, while scores of treated patients stayed constant(4).
While additional long-term studies with larger sample sizes are needed, initial studies have demonstrated that Theracurmin’s® proprietary preparation of curcumin outperforms conventional methods of curcumin isolation. In line with the company’s values, Theracurmin® is committed to assist a purpose-driven life with its superior bioavailability supported by over 30 clinical evidence.
Theracurmin Super™ – The latest from Theravalues Corporation
Theravalues Corporation takes innovation to the next level as they prepare to launch the superior curcumin formulation – Theracurmin Super™. Preliminary clinical study (meta-analysis) showed its superior bioavailability over traditional curcumin to be more than 72x. It could be the most advanced and most bioavailable form of curcumin on the market.
Disclaimers:
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. This article contains information, graphics, and data not intended for use in any regulatory applications to secure permit, license, or health claims for any countries.
—–
References:
1) What happens to the brain in Alzheimer’s Disease https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/what-happens-brain-alzheimers-disease
2) Comparative pharmacokinetics of Theracurmin, a highly bioavailable curcumin, in healthy adult subjects https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34423771/
3) Memory and brain amyloid and tau effects of bioavailable form of Curcumin in non-demented adults: A double-blind, placebo-controlled 18-month trial https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1064748117305110?via%3Dihub
4) Theracurmin supplementation may be a therapeutic option for older patients with Alzheimer’s Disease: A 6-month retrospective follow-up study https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34939543/

